
Roofing Terms Glossary: 60+ Must-Know Definitions for Roofing Business Owners
Understanding common roofing terms will help you sound professional, communicate clearly with clients and crews, and even avoid costly mistakes.
This glossary is a quick-reference guide to the most common and important roofing terms in your journey to becoming a roofer or sharpening your current skills.
Whether you’re learning about roof structure, materials, or commercial versus residential systems, you’ll find the definitions you need below.
Glossary of roofing terms (A–Z)
Scan through the terms below to get a quick crash course on all things roofing.
Pro Tip: Bookmark this page to refer back to whenever you need a quick definition.
A
Architectural shingles – A premium asphalt shingle made with multiple layers for a dimensional look. Popular in residential roofing for both durability and style.
Asphalt roofing – A type of roofing system that uses asphalt-based materials, such as shingles or roll roofing.

Asphalt shingle – The most commonly used roofing material in North America. Asphalt shingles are available in strip, laminated, or architectural varieties. Roofers can also buy and source different colors to accommodate homeowners.
B
Base sheet – The bottom layer of a roofing system in built-up or modified bitumen applications. It acts as the foundation for the rest of the roofing layers, providing extra strength, protection, and stability. This layer is usually installed directly over the roof deck or insulation and helps improve the roof’s durability and waterproofing. (This is one of the many roofing tools or supplies you’ll need to have on hand.)
Bitumen – A black, sticky substance derived from petroleum, used in roll roofing and membrane roofing systems.
C
Cap sheet – The top layer in a built-up roofing system, usually covered with granules for extra protection.
Commercial roofing – Roofing systems designed for commercial properties, usually flat or low-slope roofs using materials like TPO, EPDM, or modified bitumen.
Pro Tip: If you want to bid on more commercial jobs, make sure your professional roofing license is up-to-date according to your state requirements.
Cricket – A small ridge structure installed behind chimneys or roof penetrations to divert water.
D
Dormer – A dormer is a windowed projection from a sloped roof that creates extra space and adds architectural interest. It’s common on “cape” home styles.
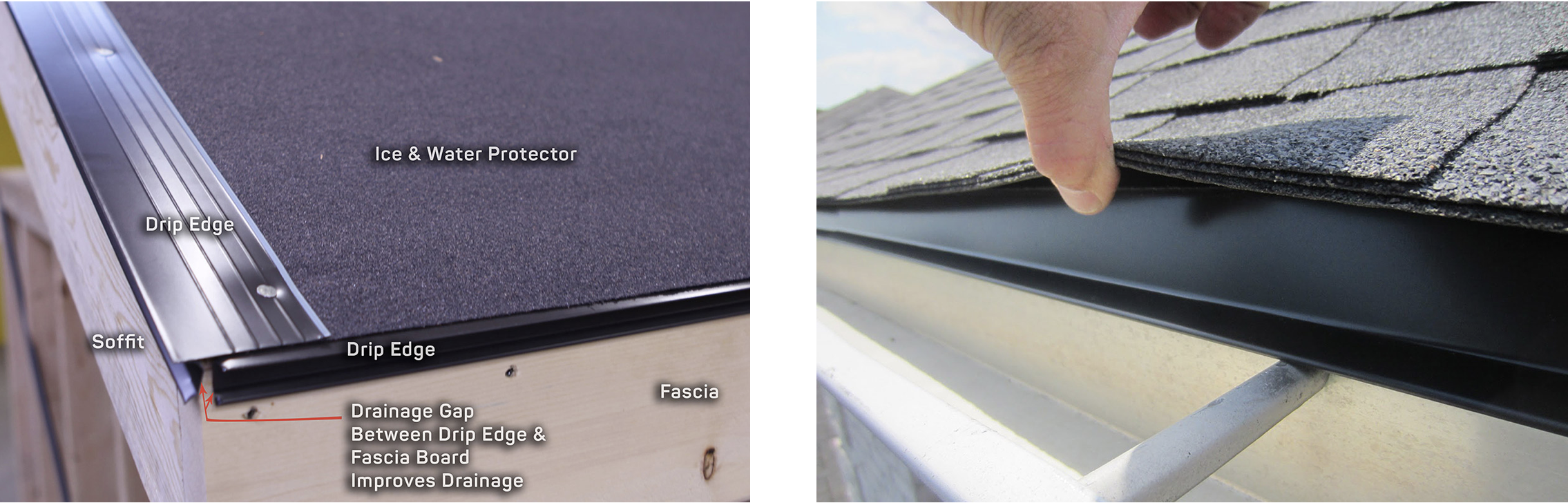
Drip edge – A metal flashing at the roof edge that helps water flow into the gutter and protects the roof deck.

E
Eaves – The lower edge of a roof that overhangs the wall, often where gutters are attached.
EPDM – A type of synthetic rubber membrane used in single-ply flat roofing systems.
F
Fascia – The vertical board along the roof edge where gutters are mounted.
Flashing – Flashing is an essential component of any roofing project. This is the thin metal or membrane material installed to prevent water from entering roof joints and penetrations.
Flat roof – A nearly level roof surface, often found on commercial buildings. Requires special drainage and membrane materials.
G
Gable roof – A common roof style with two sloping sides that meet at a ridge, forming a triangle shape at the ends.
Gutter – A system installed along the roof edge to collect and channel rainwater away from the building.
H
Hip roof – A roof where all sides slope down to the walls, with no vertical gable ends.
Hot mop roofing – A method of applying hot asphalt over layers of felt to create a waterproof flat roof.
I
Ice and water shield – A waterproof membrane applied to vulnerable roof areas to prevent leaks from ice dams and wind-driven rain.
Incline – The slope or pitch of a roof.
L
Laminated shingles – Asphalt shingles made from multiple layers for added durability and a more dimensional look.
M
Metal roofing – A durable roofing option made from steel, aluminum, or copper. Metal roofing is often used in both residential and commercial roofing projects.
Modified bitumen – A type of asphalt-based roofing membrane reinforced with fiberglass or polyester for added strength.
N
Nail pop – A nail pop happens when a roofing nail pushes up through a shingle. This is often due to poor installation or wood movement, and can even happen indoors through Sheetrock. Homeowners may spot these small circular “pops” in walls or ceilings.
P
Penetrations – Any object that goes through the roof surface, such as vents, chimneys, or skylights.
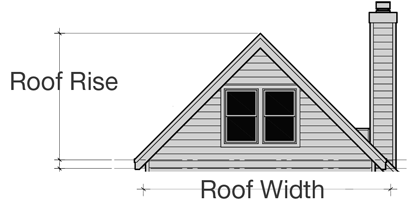
Pitch – The steepness of a roof, typically expressed as a ratio of vertical rise to horizontal run.
R
Rafters – Structural framing members that slope from the ridge to the eaves, supporting the roof deck.
Ridge – The top edge where two sloping roof planes meet.
Ridge cap – Special shingles or materials installed along the ridge to seal the joint and provide a finished look.
Roll roofing – A low-cost, rolled asphalt product used on low-slope roofs, sheds, and other simple structures.
Roof deck – The surface, usually plywood or OSB, attached to the roof framing and supporting the roofing material.
Roof edge – The perimeter of the roof where components like drip edge and fascia are installed.
Roof framing – The structural skeleton of the roof, including rafters and trusses.
Roof inspection – A thorough evaluation of a roof’s condition, often performed before repair or replacement. Roofers might offer roofing inspections for home builders and residential homeowners during the buying and selling process.
Roof replacement – The process of removing and reinstalling the entire roofing system.
Roof slope – Also called pitch, this measures how steep a roof is. It’s typically expressed as a ratio (e.g., 4:12), indicating how many inches the roof rises vertically for every 12 inches it runs horizontally.
Roofing – The process and materials used to construct or repair roofs.
Roofing contractor – A licensed professional who installs and maintains roofing systems.
Roofing material – Any product used to form the outer protective layer of the roof, including shingles, metal, or membrane.
Roofing membrane – A waterproof layer used primarily in flat or low-slope roofing systems.
Roofing project – Any installation, repair, or replacement involving a roofing system.
Roofing shingles – Overlapping pieces (typically asphalt, wood, or metal) used to cover and protect a roof.
Roofing square – A unit of measurement equal to 100 square feet of roofing area.
Roofing styles – Refers to common roof designs, like gable, hip, shed, or flat.
Roofing system – The complete setup of roof components: framing, decking, underlayment, and surface material.
READ MORE: Ready to chart your own path? Learn how to start a roofing company from the ground up.
S
Shed roof – A single-slope roof often used on home additions or outbuildings.
Shingle – A flat roofing material that overlaps in layers to provide protection from the elements.
Single-ply roofing – A flat roof system using one layer of membrane, such as TPO or EPDM. Single-ply is most often found in industrial or commercial settings.
Sloped roof – A roof with a visible incline, common in most residential homes.
Sloping roof planes – The angled surfaces of a pitched roof.
Strip shingles – Basic, single-layer asphalt shingles. A budget-friendly but less durable option.
T
TPO (thermoplastic polyolefin) – A popular single-ply roofing membrane used on commercial flat roofs.
V
Valley – The internal angle where two sloping roof sections meet. Needs special flashing to prevent leaks.
Vertical rise – The height increase in a roof’s slope, used to calculate pitch.
Keep learning with Jobber
Learning these roofing terms will help you feel more confident in the field and improve how you work with customers, suppliers, and your team.
As you grow your business, having a solid grasp of roofing terminology can help you become the expert that everyone wants to work with.
